10 Data Structures Every Developer Should Know in 2025
Knowing data structures is essential to programming whether you’re creating scalable apps or getting ready for a coding interview. They specify how information is kept, retrieved and altered, which has an immediate effect on effectiveness and performance.
The ten most important data structures that every developer should be familiar with are covered in this guide along with examples of their practical applications.
1. Arrays
A fixed size indexed collection of identically typed elements is called an array.
Use Cases: Keeping track of sequential data, such as logs, lists or scores. Indexes are used to provide elements with random access.
Example
arr = [10, 20, 30, 40]
print(arr[2])
2. Lists with links
A linear structure with nodes pointing to each other.
Use Cases:
- Allocating RAM dynamically.
- Effective additions and deletions
- particularly in stacks and queues.
Types:
- A Single-Linked List
- Double Links
- circular linked list

3. Stacks
A data structure known as Last-In-First-Out (LIFO).
Use cases
- Include undoing text editor activities.
- Parsing syntax.
- Algorithm backtracking.

4. Queues
A structure that stores components in sequence is called First-In-First-Out (FIFO).
Use cases
- Include task scheduling and printing.
- Systems for managing tasks.
- In graphs, breadth-first search.

5. Hash Tables (HashMaps)
Key value pairs are stored for quick data retrieval.
Use Cases:
- Caching
- Lookups
- Eliminating duplicates

Example
let map = new Map();
map.set(“key”, “value”);
console.log(map.get(“key”));
6. Heaps
The max/min element can be accessed easily using a certain tree based structure.
Use cases
- Priority queues.
- Heap-sort
- The shortest path algorithm developed by Dijkstra

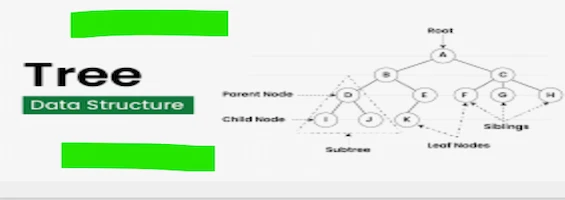
7. Trees
Structures with a hierarchy made up of nodes joined by edges.
Use cases
- file systems hierarchical data representation.
- search trees (AVL, Red-Black, Binary Search Tree).
- AI/ML decision trees.
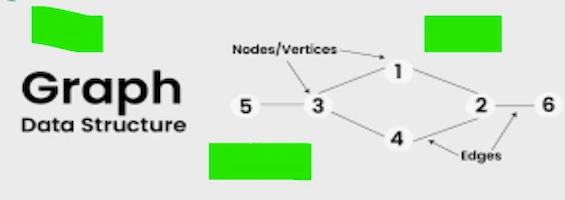
8. Graphs
A collection of vertices or nodes, joined by edges. able to be weighted or unweighted and directed or undirected.
Use cases
- Social networks.
- Routing algorithms
- Modeling the topology of networks
9. Tries (Prefix Trees)
Character by character string storage in a tree like structure.
Use cases
- Auto-complete recommendations.
- Verifying spelling
- Routing IP

10. Sets
A group of distinct components.
Use cases
- Eliminating duplication.
- Operations in mathematics (union, intersection)
- Quick membership assessments

The Significance of These Structures
Understanding these ten data structures facilitates:
- Write code more quickly and cleanly.
- Confidently solve algorithmic issues
- Get ready for technical interviews.
- Create apps that are maintainable and scalable.
These structures are common components of software engineering, regardless of the programming language you’re using Python, Java, C++, JavaScript or Go.
Concluding remarks
Learning these ten data structures will help you think like a computer scientist not just pass interviews. Your code will function better in practical scenarios if you have a more intuitive understanding of how data is arranged and accessible.










